【Steel】First Month of Export License Implementation: Impact and Current Status of Exports

Graphite electrodes are the "lifeline" of EAF steelmaking! As the core material for arc conduction and heating, they feature high conductivity and heat resistance, directly affecting molten steel quality and output. Mastering graphite electrodes means mastering the initiative in EAF steelmaking!
【Steel】First Month of Export License Implementation: Impact and Current Status of Exports
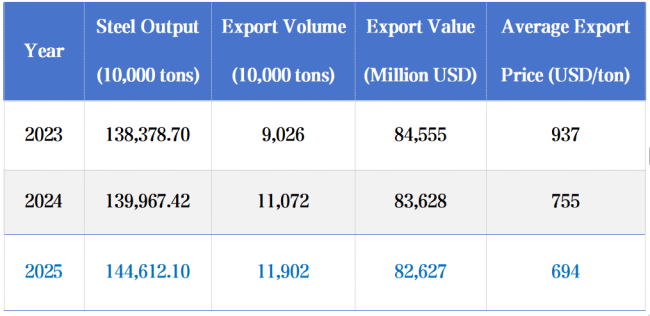
In recent years, China's real estate investment has continued to register negative growth, dragging down domestic steel consumption and leading to supply–demand imbalances. As a result, domestic enterprises have shifted their focus to overseas markets to sustain growth. Meanwhile, overseas demand from infrastructure construction and manufacturing has remained strong, particularly in emerging markets such as Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and South America. From 2023 to 2025, China's steel exports hit record highs year after year; however, export value did not rise accordingly and instead declined, with export unit prices falling—resulting in volume growth without value growth.
Data source: Mysteel data
At the same time, China's trade surplus reached USD 726.1 billion in the first three quarters of 2025. The General Administration of Customs clarified in January 2026 that China's total foreign trade value in 2025 reached a historical high, marking the ninth consecutive year of growth. Therefore, the full-year trade surplus in 2025 is highly likely to set a new historical record. The continuously expanding trade surplus has also increased the risk of exports facing anti-dumping investigations. In 2023, China faced 5–8 steel trade remedy investigation cases; in 2024, the number of new cases surged sharply to more than 36; and in 2025, cases fully erupted to over 150, of which approximately 77.78% were anti-dumping cases. The anti-dumping pressure faced by China's steel exports in 2025 was unprecedented, presenting new challenges for steel exports.
01 Restart of the Steel Export License System
On December 9, 2025, the Ministry of Commerce and the General Administration of Customs jointly issued Announcement No. 79 of 2025, announcing the implementation of export license management for certain steel products. This marked the resumption of such management measures after a 16-year hiatus. The policy officially came into effect on January 1, 2026. The main objective of the policy is to guide the optimization of the steel export structure and promote high-quality industrial development. By incorporating certain products into export license management, the policy aims to shift exports from "scale expansion" to "value enhancement," curb disorderly exports of low value-added products, and encourage enterprises toward green transformation and technological innovation. This also signifies that China's steel exports will transition from "market-driven behavior" to "policy-regulated management."
02 Steel Export License Application Process
According to the new steel export regulations effective from January 1, the license application process can be summarized as a "three-step approach."
The first step is to verify whether the product falls within the management catalog.
The second step is to apply for an electronic key and prepare the application materials.
The third step is to submit the application through the online system and wait for approval.
Among these steps, applying for the electronic key is the most critical. The main required document is the "Foreign Trade Operator Registration Record," which requires enterprises to possess import and export operation qualifications, thereby restricting "agent-based" or "buy-order" exports. Another key document is the "Product Quality Inspection Certificate issued by the manufacturer," which ensures traceability of exported products.
03 Impact of the Policy on Steel Exports
1. Higher Export Entry Thresholds, Restricting Agent-Based Exports
Before the implementation of the steel export license policy, exports could be arranged directly based on market demand and contracts, with relatively free access. Agent-based exports, with separated cargo and invoices, were convenient and low-cost. After the policy's implementation, however, only enterprises with proper export qualifications (required to apply for an electronic key) can apply for licenses from the Ministry of Commerce or designated authorities, raising the entry threshold. In practice, exports follow a "one shipment, one license" principle, meaning each license can only be used for a single customs declaration. In addition, export licenses are valid for six months and cannot be carried over to the next year.
2. More Complex Export Procedures and Reduced Timeliness
Previously, steel export procedures were relatively simple: once the contract was confirmed, goods preparation, customs declaration, and transportation followed. After policy implementation, additional steps such as license application, approval, and verification have been added, reducing export efficiency and potentially extending delivery cycles. The electronic key application typically takes around 7–10 working days; however, once obtained, the key is valid for one year and can be renewed upon expiration. Under the "one shipment, one license" system, each batch of exports requires a separate license application. Upon receipt of compliant applications, the issuing authority signs and issues the license within three working days.
3. Weakened Price Competition and Enhanced Policy Regulation
Under normal circumstances, market supply and demand determine commodity price fluctuations, and conventional export products are more market-oriented, with domestic and overseas supply–demand dynamics shaping price differentials. Traders engage in import and export based on these differentials. After policy implementation, however, the government gains a degree of regulatory control, managing export volumes by tightening or relaxing license approvals and issuance.
4. Increased Industry Concentration
With the implementation of the policy, enterprises without export qualifications are effectively excluded at the electronic key application stage. This helps curb disorderly competition by unqualified players and promotes industry consolidation and higher concentration.
5. Stricter Compliance Supervision and Trade Friction Management
In 2025, China's steel exports continued to grow, and with the trade surplus reaching record highs, more than 150 trade remedy cases were initiated throughout the year, nearly 80% of which involved anti-dumping. Following policy implementation, export product traceability has been strengthened, and exported product information must be consistent with license details, resulting in stricter compliance supervision. Additionally, by adjusting the pace and volume of license issuance, authorities can proactively manage export flows and reduce the risk of trade frictions.
04 Current Export Situation Under Policy Implementation
In December 2025, relevant authorities issued announcements implementing export license management for certain steel products, with the policy effective from January 1, 2026. During the initial policy release phase, the specific implementation details were not entirely clear, leading to a cautious market sentiment. In December, agent-based export order intake declined sharply, while leading enterprises and steel mills actively began applying for electronic keys.
Because export licenses cannot be carried over to the next year and the actual application process—from submission of materials to approval and license issuance—takes 3–5 days, port congestion increased in the first half of January following policy implementation. As procedures were gradually streamlined, congestion eased starting from the third week. It is also worth noting that agent-based export orders were still observed in January, with month-on-month volumes slightly increasing. Meanwhile, billet exports have not yet shown a significant impact from the policy.
Overall, during the first month of implementing the steel export license policy, the market is undergoing a period of "short-term adjustment" while seeking a new equilibrium under the new rules. In the first quarter of 2025, China's steel exports totaled 27.42 million tons. Under the impact of the new policy, it is expected that China's steel exports in the first quarter of 2026 may decline, with an estimated decrease of 15%–20%.
Feel free to contact us anytime for more information about the EAF Steel market. Our team is dedicated to providing you with in-depth insights and customized assistance based on your needs. Whether you have questions about product specifications, market trends, or pricing, we are here to help.
No related results found








0 Replies