Application of graphite material in aerospace

The application and suggest of development of graphite materials in aerospace are briefly introduced.
As a non-metallic resource mineral, graphite is widely used in the aerospace field due to its self-lubricating properties, easy forming and processing, good thermal conductivity, thermal stability, and stable chemical properties. Such as sealing materials, throat lining materials, etc. This article mainly discusses the application and prospect of graphite materials in the aerospace field.
1 Application of graphite materials in the aerospace field
1.1 Sealing material
The performance of the sealing material directly determines the reliability of the seal. With the development and progress of science and technology, more and more stringent requirements are put forward for sealing materials. As the space station has severe environmental changes such as high temperature, low temperature, high pressure, microgravity and corrosion, the sealing materials of the space station are mainly used in the propulsion system of the spacecraft, the sealing of structural components such as wing ends and elevons, as well as hydraulic system and pneumatic system in the box, valves and other parts of the static seal and dynamic seal. However, due to the fast rotation of the engine shaft, the graphite material cannot meet the requirements for the tensile strength of the sealing material, so the graphite material cannot be used for the shaft seal material.
(1) Flexible graphite material
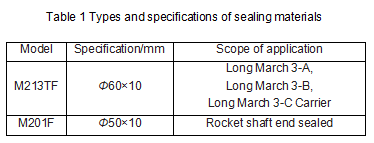
In the mid-1980s, the United States successfully developed a flexible graphite material made by deep processing of natural flake graphite. Flexible graphite material has good self-lubricating properties and thermal conductivity, small linear expansion coefficient and friction coefficient, and large chemical inertness, which can replace asbestos and rubber materials, and has been successfully applied to sealing materials in high-tech fields. Flexible graphite material has the characteristics of high compressibility and resilience, but its strength is extremely low and can only be applied to low-pressure static sealing. The types and specifications of sealing materials for several liquid rocket engines are shown in Table 1.
(2) Reinforced graphite material
The sealing performance of graphite material is poor, and other materials (such as resin, metal, etc.) need to be impregnated with graphite to improve its sealing performance.
(a) Resin impregnation: The resin is generally phenolic resin, tetrahydrofuran and furfurone resin. Jia Qian, etc. studied the friction and wear characteristics of graphite impregnated with phenolic resin under different conditions and concluded that the sealing material of liquid rocket engine turbopump should have a moderate degree of graphitization; Song YZ, etc. obtained graphite material from mesophase carbon microspheres (MCMBS) impregnated with resin and asphalt, and then carbonized this graphite material at 500 °C to obtain a reinforced material. It is found that the increase of impregnation and carbonization period makes the porosity of the material decrease, the density increase, the bending strength of the material increase, and the sealing performance is excellent, so it has a good application prospect in liquid rocket engine.
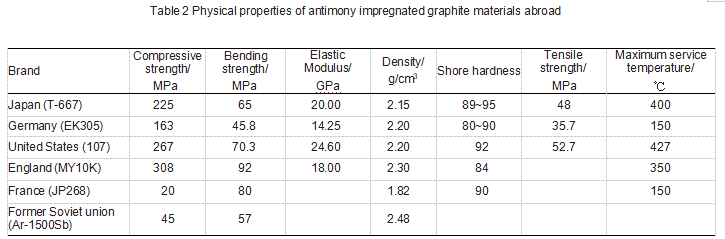
(b) Metal impregnation: Metal impregnated graphite can maintain the advantages of both. Commonly used impregnated metals are antimony, silver, lead, copper, etc. The physical properties of antimony-impregnated graphite materials have been tested abroad. The related research is shown in Table 2.
(c) Inorganic salt impregnation: Graphite materials are prone to oxidation reactions above 300°C, which makes the mechanical properties of the material worse. After impregnation with inorganic salts, the high temperature oxidation resistance of graphite is significantly improved. Shanxi Coal Chemistry Research Institute used 13μm natural graphite powder, 3μm BN powder, pitch with a softening point of 175°C, 320μm petroleum coke powder and phenolic resin to prepare sealing materials. First, the powders were mixed in a certain proportion and then formed by hot pressing, the graphite material obtained by impregnation and carbonization of phenolic resin has a wide range of applications in aviation and aerospace end face sealing and other anti-friction materials.
(3) Isotropic graphite material
Isotropic graphite material originated in the 1960s. Compared with other graphite materials, the comprehensive performance of isotropic graphite material is better, and the forming process is also different. Generally, the cold isostatic press is used as the equipment, and the petroleum coke and asphalt coke are specially treated as raw materials. The isotropic graphite material prepared has the characteristics of high compressive strength and bending strength, uniform and dense structure, high density, extremely high precision and smoothness of the sealing surface after processing, and low opening rate, so it is also called high density and high strength graphite material. Russia uses isotropic pyrolysis graphite material as a sealing material in the turbopump of a new generation of high-thrust aerospace engine. The sealing performance of the sealing ring is good, and currently there has been no leakage accident. At present, raw materials and molding processes are the key to the research of isotropic graphite materials. Our country has also developed and researched isotropic graphite materials for more than 30 years. Although there have been some advances in production scale and technology, there is still a certain gap compared with foreign countries.
1.2 Throat lining material
The characteristics of graphite material, such as high temperature resistance, ablation resistance and light weight, provide conditions for it to become a small rocket solid rocket motor (SRM) throat lining material. In the late 1940s, solid sounding rockets in the United States were the first to use graphite throat linings. Later, the first generation of throat lining materials (ATJ high-strength graphite materials), the second generation of throat lining materials (G-90 high-density and high-strength graphite materials), and the third generation of throat lining material (Graphnol isotropic graphite material) appeared one after another.
In the early 1960s, the silicon-infiltrated KS-8 high-strength graphite material jointly developed by the Institute of Metal Research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an Aerospace Composite Materials Research Institute and Jilin Carbon Factory can be used as the first-generation throat lining material. KS-8 graphite throat lining material successfully solved the problem of hot cracking due to excessively thick silicon infiltrated layer. Since then, the research on SRM has shifted from basic to model, laying a solid foundation for later throat lining materials. KS-8 graphite throat lining material has been successfully applied to the final SRM of Dongfanghong-I.
With the continuous improvement of all aspects of SRM requirements, graphite throat lining materials also need to improve their ablation resistance. In the mid-1960s, our country’s first generation of throat lining material T704 high-density and high-strength graphite material was independently developed by Shanxi Coal Chemistry Research Institute, Harbin Electric Carbon Research Institute and Xi’an Aerospace Composite Materials Research Institute. In the early 1980s, the T705 graphite material jointly developed by Harbin Electric Carbon Research Institute and Xi’an Aerospace Composite Materials Research Institute has greatly improved its ablation resistance. It has been widely used in high temperature and oxidation resistant parts such as SRM throat lining of various small tactical bombs.
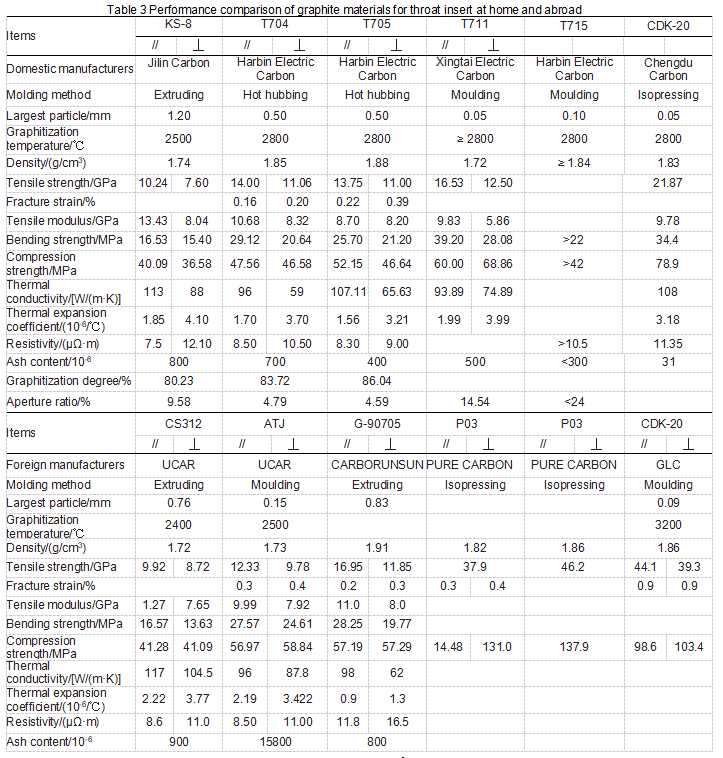
T707, T715 and T711 graphite materials have ablation resistance and can also be used as throat lining materials for small rocket SRMs, and belong to the second generation of throat lining materials in our country. The isotropic CDK-20 graphite material developed by Chengdu Carbon Co., Ltd. can be used as the third-generation throat lining material of the small rocket SRM by using the isostatic pressing process. Application research is ongoing. Table 3 shows the performance comparison of graphite materials used for throat lining at home and abroad.
In addition, the graphite copper infiltration material (carbon/copper composite material) prepared by using the coarse-grained high-strength graphite as the substrate and the graphite crucible pressure copper infiltration process directly on the substrate at high temperature is also used as the throat of the solid rocket motor Lining material.
The main technical indicators of graphite copper infiltration materials:
Bulk density: 1.75~1.80 g/cm3;
Compressive strength: ≥38 MPa;
Obvious porosity: ≥10%;
Ash content: ≤0.1%;
Graphitization degree: ≥70%.
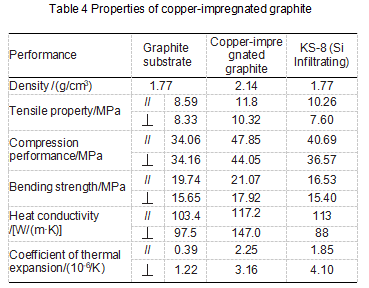
The material properties before and after copper infiltration are shown in Table 4, talk with us for more related technical news.
No related results found








0 Replies