Technology sharing--Cooling method of graphitization furnace

Technology sharing--Cooling method of graphitization furnace
During the operation of graphitization furnace, the furnace temperature reaches more than 2300 ℃, and the end connected between conductive electrode and furnace core works at such high temperature. Suppling the professional Graphite electrode products. The other end of the conductive electrode is connected with the copper bus, which ensures that the temperature at the connection with the copper plate is lower than the melting temperature of the copper plate. At the same time, because the conductive electrode is exposed in the air, it must work below the oxidation temperature. For this reason, forced cooling must be carried out. At present, there are basically two cooling methods.


1. Direct water cooling:
A drilled water pipe is placed horizontally on the conductive electrode, and the connection between the conductive electrode and the copper bus is watered to cool it. This direct cooling method is simple, convenient and has good cooling effect. The disadvantage is that the cooling water splashes everywhere, which is easy to seep into the furnace body. Moreover, a drainage tank needs to be installed in this way. The tank is easy to be blocked. If it is not treated in time, the water in the tank is easy to penetrate into the furnace, and the spray water is also easy to penetrate into the furnace, so as to shorten the life cycle of the furnace and oxidize the products in the furnace. In addition, in the north, it is easy to freeze around the water tank in winter, which is difficult to deal with.
2. Direct internal cooling:
After boring the conductive electrode, plug it directly with a screw plug, and then connect two water pipes, one long and one short, so that the water can flow directly to the round hole of the electrode and then be discharged.
In the above sense, artificial graphite can only be called a kind of "polycrystalline graphite". However, this "polycrystalline graphite" has the basic characteristics of ideal graphite.
Crystal structure of diamond
In the crystal structure of diamond, each carbon atom is covalently combined with four adjacent carbon atoms, which is positively tetrahedral coordination and belongs to equiaxed crystal system. Diamond is a typical atomic crystal. Such structural characteristics of diamond determine that diamond does not conduct electricity and has poor thermal conductivity. When heated to 1000℃ without air, diamond will change into graphite structure. When heated to 780 ℃ in air, it will burn and produce carbon dioxide. Synthetic diamond can be obtained by using high purity synthetic graphite at high temperature and high pressure, but the particles of this synthetic diamond are relatively small.
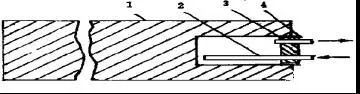
Fig. 1-7 Schematic diagram of diamond crystal structure
The advantage of this way is that it is easy to make the water system into a fully closed or semi-closed system, and will not penetrate into the furnace. Because the drainage tank can not be used, manufacturers using this method often make the water system into a semi closed system. The disadvantages are: cooling effect is not as good as direct drenching water cooling, higher requirements for water quality, water shortage is strictly prohibited. Otherwise, when the furnace head temperature rises and cold water is suddenly introduced, it is easy to produce water explosion, which is very dangerous.
Graphitization furnace side wall is divided into fixed wall and movable wall
The fixed side wall is generally built with refractory bricks, and a row of air holes shall be reserved at certain intervals to enable the flue gas in the furnace core to be discharged smoothly during power transmission. Using firebrick as side wall has good thermal insulation effect and slightly longer service life, but the cost is relatively high.
The movable side wall is made of cement, clay and firebrick fragments in a certain proportion, and an exhaust hole is reserved on the wall. When in use, the movable side wall is hung on both sides of the furnace and between the columns made of channel steel. The movable side wall has the advantages of economy, labor saving and convenient cooling of the furnace. The disadvantages are that it is not resistant to mechanical shock and thermal shock, and the damage can not be repaired.
In addition, now there are hybrid side walls with fixed lower half and movable upper half, which take into account the advantages of both and have ideal use effect.
Channel steel (or cast iron support) is mainly used to fix the side wall. The electrified furnace core is composed of heated products and resistance materials filled in the middle. After power on, the furnace body has a certain thermal expansion force, contact us for further graphite technical guidance.
No related results found








0 Replies