Analysis of the shutdown of Acheson graphitization furnace

1 Existing problems and analysis
The ideal shutdown control method of the Acheson graphitization furnace should be determined according to the furnace core temperature. Get the high quality (UHP) graphite electrodes. However, due to the non-uniformity of the graphitization furnace core temperature, the high temperature is not easy to control, it is difficult to achieve continuous automatic measurement. Therefore, at this stage, Acheson graphitization furnaces all use the power transmission curve of constant power distribution to control the rise rate of the furnace core temperature, and the cumulative power will eventually reach the planned power as the basis for the power outage. This method has many defects, and it is extremely unscientific. It often happens that the furnace core temperature has reached, but the power transmission has not reached the specified value. Continued power transmission will cause a great waste of power, fail to achieve the purpose of energy saving, and even cause poor product quality in the furnace;
Sometimes it may happen that the temperature of the furnace core has not fully reached the high temperature required for the product to complete the graphitization process, but the power transmission has reached the planned power. At this time, the furnace is shut down, resulting in insufficient graphitization of the product, resulting in high product resistivity.
2 Improvement measures
2.1 Judging the furnace shutdown based on the furnace resistance rise rate
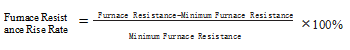
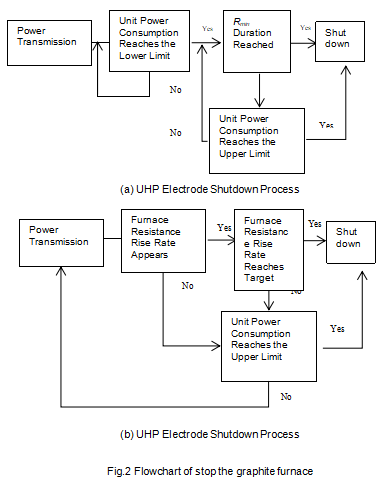
In the graphitization production of ultra-high power (UHP) graphite electrodes, after reaching the lowest furnace resistance, in order to capture the obvious signs of furnace resistance rise, and considering the correlation between furnace resistance rise rate and graphitized product resistivity, this method is adopted. Practice shows that the higher the furnace resistance rise rate, the lower the resistivity of graphitized products.
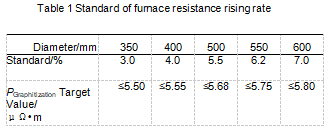
UHP electrode product specifications are different, the standard of furnace resistance rise rate is also different, and the resistivity of corresponding graphitized products is also different. According to actual production experience, the furnace resistance rise rate standard is shown in Table 1.
2.2 Shut down the furnace according to the minimum furnace resistance duration
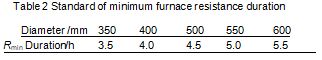
In UHP electrode graphitization production, the furnace resistance rise rate standard is used as an important basis for the judgment of furnace shutdown; for quasi-super high power (SHP) graphite electrodes, after reaching the minimum furnace resistance, if the power continues to be supplied, the minimum furnace resistance remains after a period of time, the resistance of the furnace will rise. After the resistance of the furnace reaches the rising area, no power can be supplied, because after the resistance of the SHP electrode rises, it is easy to cause electro-oxidation (current breakdown of the air generates a high-temperature arc, resulting in sublimation of carbon around the electrode, produce serpentine oxidation), so the SHP electrode is based on the minimum furnace resistance duration as an important basis for the judgment of furnace shutdown. Since the duration of the minimum furnace resistance is related to the resistivity of the graphitized product, this method is adopted. Practice has shown that the longer the minimum furnace resistance lasts, the lower the resistivity of the graphitized product. Different product specifications have different minimum furnace resistance durations. According to actual production experience, the minimum furnace resistance duration standard is shown in Table 2.
2.3 Judging the shutdown according to the standard of electricity consumption( superior limit)
When the furnace resistance rise rate is used to judge that the change in furnace resistance cannot be reproduced when the furnace is stopped, the unit power consumption standard (superior limit) is used to judge the furnace shutdown. The purpose of this is to use the previous unit power consumption standard (superior limit) as a supplementary condition. To ensure that the graphitized product can not only achieve the expected physical and chemical properties, but not excessive graphitization. Facts have proved that the use of electricity unit consumption standard (superior limit) to shut down the furnace is also reliable.
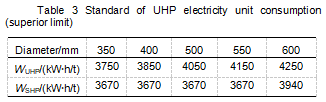
Due to different product specifications, the power consumption standard (superior limit) is also different. According to the actual production experience, the unit consumption standard (superior limit) of electricity is shown in Table 3 talk with us for more technical guidance.
2.4 Graphitization shutdown judgment process
Figure 2 shows the judgment process of graphitization shutdown.
No related results found








0 Replies