What is the difference between graphitization and carbonization?

What is the difference between graphitization and carbonization?
1. What is graphitization?
Graphitization is an industrial process in which carbon is converted to graphite. This is a change in the microstructure of carbon or low alloy steel, which is exposed to a temperature of 425 to 550 ℃ for a long time, such as 1000 hours. This is a kind of embrittlement. Graphite electrode is electric furnace steelmaking, green and environmental. For example, the microstructure of carbon molybdenum steel usually contains pearlite (a mixture of ferrite and cementite). When this material is graphitized, pearlite will be decomposed into ferrite and randomly dispersed graphite. This leads to steel embrittlement, and when these graphite particles are randomly distributed throughout the matrix, it leads to a moderate reduction in strength. However, we can prevent graphitization by using materials with higher resistance that are less sensitive to graphitization In addition, we can modify the environment (for example, by increasing the pH value or reducing the chloride content). There is another method to prevent graphitization, which includes the use of coating. Cathodic protection of cast iron.
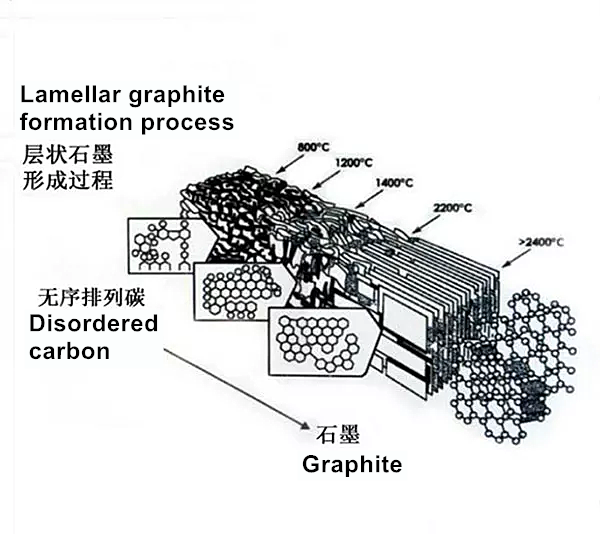
2. What is carbonization?
Carbonization is an industrial process in which organic matter is converted to carbon. The organics we consider here include plants and animal carcasses. This process occurs by destructive distillation. This is a pyrolysis reaction, which is considered to be a complex process. In this process, we can observe many simultaneous chemical reactions. For example, dehydrogenation, condensation, hydrogen transfer and isomerization. The carbonization process is different from the carbonization process because carbonization is a faster process because its reaction speed is many orders of magnitude faster. Generally, the applied heat can control the degree of carbonization and the residual content of foreign elements. For example, at a temperature of 1200 K, the carbon content of the residue is about 90% by weight, and at a temperature of about 1600 K, the carbon content of the residue is about 99% by weight. Generally, carbonization is an exothermic reaction. We can make it self-sustaining or use it as an energy source that does not form any trace of carbon dioxide gas. However, if biomaterials are exposed to sudden changes in heat (such as in a nuclear explosion), the biomaterials will carbonize as soon as possible and become solid carbon.

3. What is the difference between graphitization and carbonization?
Graphitization and carbonization are both industrial processes that involve carbon as a reactant or product. But carbonization involves the conversion of organic matter into carbon, while graphitization involves the conversion of carbon into graphite. Therefore, carbonization is a chemical change, while graphitization is a microstructure change. For professional guidance on carbon technology, please contact us for details.
No related results found








0 Replies