【Graphitized Carburant】Testing Methods and Applications

【Graphitized Carburant】Testing Methods and Applications
1. Introduction to Graphitized Carburant
Graphitized carburant is a carbon-containing material added to compensate for carbon loss during steelmaking. Its main component is a carbon product whose molecular structure has been altered through high temperatures or other methods. The characteristics of graphitized carburant include:
· High fixed carbon content, which effectively increases the carbon content and strength of steel
· Low ash content, which reduces impurities and oxide formation in steel
· Low moisture content, which lowers the solubility of hydrogen and the porosity in steel
· Low sulfur content, which reduces the formation of sulfides and brittleness in steel
· Low chlorine content, which minimizes corrosion from chlorides and stress corrosion cracking in steel
2. Applications of Graphitized Carburant
Graphitized carburant is widely used in metallurgy, casting, machinery, and chemical industries.Its main uses include:
· As a carbon addictives during steelmaking to enhance the quality and performance of steel
· As a cover agent in casting to protect the surface of castings from oxidation and nitriding
· As a lubricant in machining to reduce friction and wear
· As a catalyst or carrier in chemical processes to improve reaction efficiency and product quality
3. Testing of Graphitized Carburant
According to the YB/T 4403-2014 Graphitized Carburant standard, the product specifications are shown in Table 1.
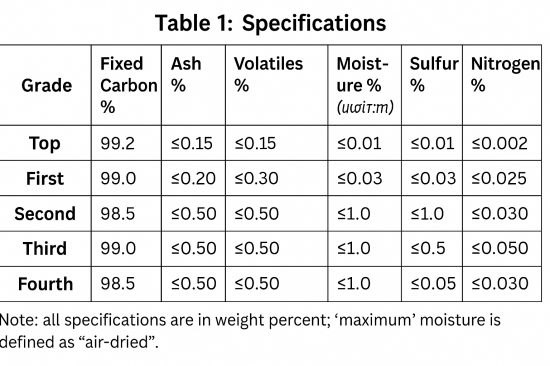
The main aspects of graphitized carburant testing include:
3.1 Appearance
The appearance should be black or dark gray granules or powder, without visible impurities. Appearance testing can be performed visually or with a microscope, evaluating shape, color, luster, and purity.
3.2 Particle Size Distribution
The particle size should meet user requirements or be mutually agreed upon. Testing can be done using a laser particle size analyzer to determine the proportion of different size ranges, average particle size, and maximum size.
3.3 Fixed Carbon Content
Measured according to GB/T 3521. The minimum limit should meet user requirements or mutual agreement. Testing uses high-temperature combustion: the sample is heated in air to ~1000°C to completely burn off volatile matter, the residue is weighed, and the percentage of fixed carbon is calculated.
3.4 Ash Content
Also measured according to GB/T 3521. The maximum limit should meet user requirements or mutual agreement. The test involves heating the sample in air to ~800°C to burn off carbon content completely, then weighing the residue and calculating the ash content percentage.
3.5 Moisture Content
Measured according to GB/T 24527. The maximum limit should meet user requirements or mutual agreement. The test uses the drying method: the sample is dried at ~105°C until constant weight, then weighed to calculate moisture content percentage.
3.6 Sulfur Content
Measured according to GB/T 24526. The maximum limit should meet user requirements or mutual agreement. The test uses the Eschka method or coulometric method: the sample is mixed with iron oxide and oxidized at high temperature to form SO₂, which is then titrated with iodine solution or measured electrolytically, calculating sulfur content percentage.
3.7 Nitrogen Content
According to Appendix A of YB/T 4403-2014, nitrogen content is measured using an oxygen-nitrogen analyzer.
4. Sample Requirements
The quantity and quality of test samples vary by method, but general principles include:
· Samples must be representative of the whole batch
· Sample quantity must be sufficient for all required tests
· Samples must remain intact, unpolluted, and undamaged
· Samples should be properly stored to prevent moisture absorption or degradation
· Samples should be prepared as specified to ensure uniformity and stability
5. Standards and Specifications for Graphitized Carburant Testing
· YB/T 4403-2014 Graphitized Carburant: Defines terminology, technical requirements, test methods, inspection rules, marking, packaging, transportation, and storage
· GB/T 3521-2008 Chemical Analysis Methods of Graphite: Covers analysis of moisture, volatile matter, ash, fixed carbon, sulfur, and acid-soluble iron in graphite products
· YB/T 5189-2007 Determination of Volatile Matter in Carbon Materials: Specifies principles, equipment, procedures, results, and precision of volatile content testing
· GB/T 24527-2009 Determination of Internal Moisture in Carbon Materials: Defines internal moisture, instruments, sample preparation, test procedures, result calculation, and precision
· GB/T 24526-2009 Determination of Total Sulfur in Carbon Materials: Specifies Eschka and coulometric methods, including principles, reagents, equipment, procedures, and precision
· GB/T 1427-2006 Particle Size Analysis of Carbon Materials: Details sieve and laser particle size analysis methods, including principles, sample preparation, procedures, result calculation, and precision
Feel free to contact us anytime for more information about the graphitized petroleum coke carburant (GPC) market. Our team is dedicated to providing you with in-depth insights and customized assistance based on your needs. Whether you have questions about product specifications, market trends, or pricing, we are here to help.
No related results found








0 Replies